그렇다면 2026년, 환율 변화는 글로벌 무역 환경을 어떻게 바꿔놓게 될까요?
FX (Foreign Exchange) is one of the most practical indicators for understanding the global economy and trade environment in 2026.
As economic growth continues to slow, shifts in interest rates, capital flows, and monetary policy are having a direct impact on manufacturing and export-driven industries. In particular, exchange rate volatility is becoming a core strategic factor for companies operating within global supply chains.
How will changes in FX reshape the global trade environment in 2026?
2026년 세계경제 전망을 더 잘 이해하고 싶다면,
2025년 한국 수출입 흐름을 정리한 Ep.1을 먼저 참고해 보세요!
If you want a better understanding of the global economic outlook for 2026,
we recommend starting with Ep.1, which outlines Korea’s 2025 export and import trends.
2026년 세계경제 전망: 성장 둔화 속 차별화
2026 Global Economic Outlook: Differentiation amid Slowing Growth
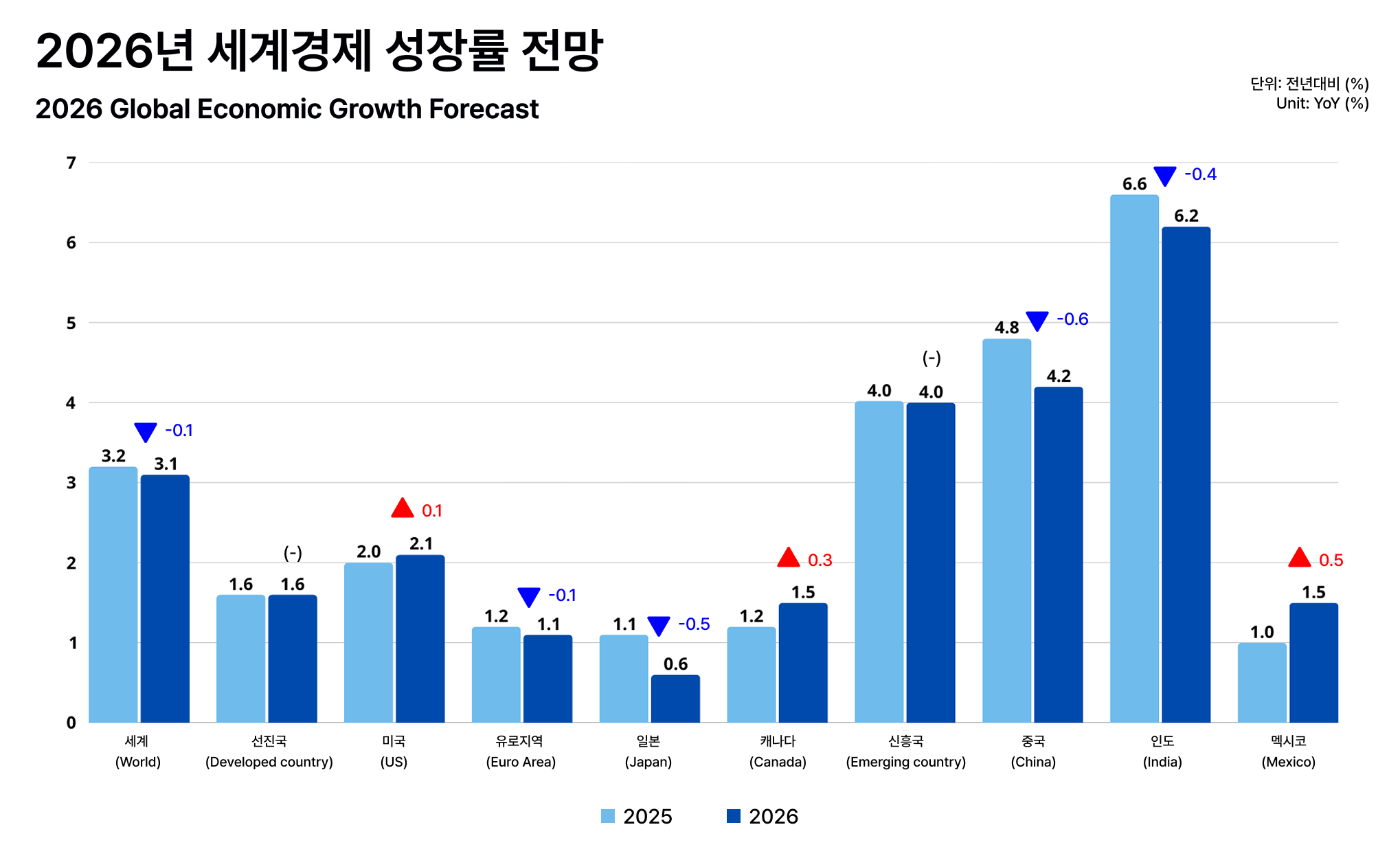
한국무역협회 국제 무역통상연구원의 「2026년 세계경제 및 무역환경 전망」에 따르면,2026년 세계 경제성장률은 2.9~3.1% 수준으로 예상되며, 2025년에 비해 전반적으로 완만한 성장 둔화 국면이 이어질 것으로 전망됩니다. 미국의 관세 정책 영향이 일부 지연되면서 2025년 세계 경제는 당초 예상보다 견조한 흐름을 보였으나, 지정학적 리스크와 금융 환경 불확실성이 여전히 해소되지 않은 만큼 2026년에는 성장세 둔화가 불가피할 것으로 보입니다.
다만 이러한 흐름이 모든 국가에 동일하게 적용되기보다는, 각국의 정책 방향과 산업 구조에 따라 성장 경로는 차별화될 가능성이 큽니다. 특히 인도는 인프라 투자 확대와 기술 산업 성장을 바탕으로 2026년에도 약 6% 수준의 비교적 높은 성장률을 기록할 것으로 전망됩니다. 이는 글로벌 무역 구조 내에서 신흥국의 역할이 점진적으로 확대되고 있음을 시사하는 대목입니다.
According to the 2026 Global Economy and Trade Outlook published by the Korea International Trade Association (KITA), global economic growth in 2026 is expected to range between 2.9~3.1%, indicating that a phase of moderate growth slowdown is likely to continue compared to 2025. While the impact of U.S. tariff policies was partially delayed, allowing the global economy to show more resilience than initially anticipated in 2025, geopolitical risks and uncertainty in the financial environment have yet to be resolved. As a result, a slowdown in global growth appears unavoidable in 2026.
However, this trend is unlikely to affect all countries in the same way. Growth paths are expected to diverge depending on national policy directions and industrial structures. In particular, India is projected to record a relatively high growth rate of around 6% in 2026, supported by expanded infrastructure investment and continued growth in technology industries. This suggests that the role of emerging economies within the global trade structure is gradually expanding.
성장 둔화 이후, 무역 환경은 어떻게 달라질까
How Will the Trade Environment Change After Slowing Growth

이러한 성장 둔화 국면에서 보다 주목할 점은 경제 성장률 자체보다 성장의 ‘질’과 ‘전개 방식’이 변화하고 있다는 점입니다. 주요 선진국을 중심으로 투자와 무역 여건에 대한 불확실성이 지속되면서, 성장 동력은 점차 내수·정책·산업 구조에 의해 좌우되는 양상을 보이고 있습니다. 이는 글로벌 경제가 동조화된 회복 국면보다는, 국가·지역별로 상이한 흐름을 보이는 국면에 접어들었음을 의미합니다.
특히 이러한 차별화된 성장 경로는 무역 환경과 환율 변동성을 통해 더욱 분명하게 드러날 가능성이 큽니다. 통상 정책 불확실성과 관세 효과가 누적되는 가운데, 글로벌 교역은 과거와 같은 동반 회복보다는 제한적인 확장에 그칠 것으로 예상됩니다. 다시 말해 2026년 세계경제는 성장률 숫자보다, 무역 구조와 교역 조건의 변화가 경제 흐름을 해석하는 핵심 변수로 작용하는 해가 될 가능성이 높습니다.
In a period of slowing growth, what deserves greater attention is not the economic growth rate itself, but the changing quality and pattern of growth. As uncertainty surrounding investment and trade conditions persists across major advanced economies, growth drivers are increasingly shaped by domestic demand, policy direction, and industrial structure. This indicates that the global economy is moving away from a synchronized recovery phase toward one characterized by divergent trends across countries and regions.
These differentiated growth paths are likely to become more evident through changes in the trade environment and rising exchange rate volatility. Amid ongoing uncertainty in trade policy and the cumulative effects of tariffs, global trade is expected to experience only limited expansion rather than a broad based recovery. In other words, in 2026 the global economy is likely to be shaped less by headline growth figures and more by changes in trade structures and trading conditions, which will serve as key variables in interpreting overall economic trends.
주요 국가별 경제 흐름과 무역 환경
Economic Trends and Trade Environment Across Major Economies
2026년 세계경제가 완만한 둔화 국면을 이어가는 가운데, 미국·EU·중국은 각기 다른 정책 환경과 구조적 제약 속에서 상이한 성장 경로를 보일 가능성이 큽니다. 특히 주요국의 경기 흐름은 무역 조건과 환율 변동성에 직접적인 영향을 주기 때문에, 수출입 전략을 수립하는 기업 입장에서는 국가별 리스크 요인을 분리해 해석할 필요가 있습니다.
As the global economy continues to experience a phase of moderate slowdown in 2026, the United States, the EU, and China are expected to follow different growth paths shaped by distinct policy environments and structural constraints. In particular, economic conditions in major economies have a direct impact on trade terms and exchange rate volatility. From the perspective of companies formulating export and import strategies, it is therefore essential to analyze country specific risks separately rather than interpreting global trends as a single uniform movement.
미국: 성장과 조정의 공존
United States: Coexistence of Growth and Adjustment

상방 요인
미국 경제는 AI 투자 지속, 생산성 향상, OBBBA(One Big Beautiful Bill Act)에 따른 경기 부양 효과, 금리 추가 인하 가능성, 제조업 리쇼어링 등 요인에 힘입어 성장 하방을 일정 부분 방어할 수 있을 것으로 보입니다. 특히 OBBBA는 2025년에 서명된 연방 세제·지출·보건 정책 개혁 법안으로, 2017년 세제개편법(TCJA)을 연장하고 새로운 조치를 통해 기업 활동과 투자 여건을 지원하는 효과가 기대됩니다.
하방 요인
반면 노동시장 둔화, 실질소득 감소, 물가 부담 지속, 빅테크 기업 실적 둔화 가능성 등은 미국 경제의 하방 리스크로 작용할 수 있습니다. 이에 따라 AI 관련 주식을 중심으로 주식시장의 고평가 조정 가능성도 배제하기 어렵습니다.
Upside Factors
The U.S. economy is expected to cushion downside growth risks to some extent, supported by continued AI investment, productivity gains, the stimulative effects of the OBBBA (One Big Beautiful Bill Act), the possibility of additional interest rate cuts, and ongoing manufacturing reshoring efforts. In particular, the OBBBA, a federal reform package covering tax, spending, and healthcare policies signed into law in 2025, extends the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) while introducing new measures aimed at supporting corporate activity and improving investment conditions.
Downside Factors
At the same time, factors such as a slowdown in the labor market, declining real incomes, persistent inflationary pressures, and the potential weakening of performance among big tech companies could act as downside risks to the U.S. economy. In this context, the possibility of a valuation adjustment in equity markets, particularly among AI related stocks, cannot be ruled out.
EU : 회복과 불확실성의 공존
EU: Coexistence of Recovery and Uncertainty

상방 요인
EU는 안정적인 노동시장과 목표 인플레이션 수준 도달에 따른 실질 구매력 개선, 그리고 NGEU(NextGenerationEU) 기금을 통한 공공투자 지속이 성장 하방을 지지할 요인으로 평가됩니다. NGEU는 코로나19 이후 경제 회복을 위한 대규모 회복 계획으로, 녹색·디지털 전환을 중심으로 기술·교육 분야에 대한 투자를 포함하고 있습니다.
하방 요인
다만 유로화 강세 가능성, 정치적 불확실성 확대, 국방비 지출 증가, 미국과의 무역 마찰 등은 경제 불확실성을 키우는 요인으로 작용할 수 있습니다. 또한 ECB가 금리 인하 사이클 종료를 검토할 경우, 통화 정책 측면에서의 추가적인 성장 지원 여력은 제한될 수 있습니다.
Upside Factors
The EU’s growth outlook is supported by a stable labor market, improvements in real purchasing power as inflation approaches target levels, and the continued implementation of public investment funded through the NGEU (NextGenerationEU) program. NGEU represents a large scale recovery initiative launched in response to the COVID 19 crisis and focuses on promoting green and digital transitions, including investment in technology and education.
Downside Factors
At the same time, potential euro appreciation, rising political uncertainty, increased defense spending, and the risk of trade frictions with the United States could contribute to heightened economic uncertainty. In addition, if the ECB considers bringing its interest rate easing cycle to an end, the scope for further growth support from monetary policy may become more limited.
중국 : 정책부양에도 구조적 한계
China: Structural Constraints Despite Policy Support

상방 요인
중국은 대규모 인프라 투자 확대와 함께 첨단 제조업 및 신산업 육성을 통해 성장 둔화를 완화하려는 정책 기조를 유지할 것으로 보입니다. 수출시장 다변화와 내수 활성화 정책 역시 단기적으로는 경기 회복을 뒷받침하는 요인으로 작용할 가능성이 있습니다.
하방 요인
반면 부동산 시장 침체가 장기화되고, 반내권(anti-involution) 캠페인에 따른 투자 위축, 미·중 간 통상 마찰 가능성은 여전히 구조적 제약 요인으로 남아 있습니다. 다만 미·중 정상 간 합의를 통해 일부 불확실성이 완화될 경우, 희토류 수출 통제 유예나 첨단 반도체 수출 허용과 같은 제한적 긍정 요인이 나타날 가능성도 존재합니다.
Upside Factors
China is expected to maintain a policy stance aimed at easing growth slowdown through expanded large scale infrastructure investment, along with continued support for advanced manufacturing and emerging industries. Efforts to diversify export markets and stimulate domestic demand may also provide short term support for economic recovery.
Downside Factors
At the same time, a prolonged downturn in the property market, investment contraction linked to the anti involution campaign, and the risk of renewed trade tensions between the United States and China remain key structural constraints. That said, if bilateral agreements between the U.S. and China help ease some uncertainties, limited positive developments such as temporary relief from rare earth export controls or approval for exports of advanced semiconductor products could emerge.
환율과 무역 환경의 변화: 회복보다 구조적 재편의 흐름
Changes in the Exchange Rate and Trade Environment: Structural Reconfiguration Rather than Recovery
2026년 글로벌 경제 환경에서 환율과 무역은 특정 방향성보다는 변동성과 구조 변화가 상수로 작용하는 국면으로 해석할 필요가 있습니다. 주요국의 정책 대응과 성장 둔화가 맞물리면서, 환율은 경기 지표보다 무역 조건과 기업 수익성에 더 직접적인 영향을 미치는 변수로 부각되고 있습니다. 원/달러 환율은 글로벌 자본 이동과 해외 투자 확대 흐름 속에서 과거 대비 높은 수준에서 등락을 이어갈 가능성이 제기되며, 이는 수출과 수입 기업에 상반된 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
In the global economic environment of 2026, exchange rates and trade should be interpreted as entering a phase in which volatility and structural change act as constant factors, rather than following a clear directional trend. As policy responses across major economies intersect with slowing growth, exchange rates are emerging as variables that exert a more direct influence on trade conditions and corporate profitability than conventional economic indicators. The KRW/USD exchange rate is expected to continue fluctuating at levels higher than in the past amid global capital movements and expanding overseas investment, resulting in contrasting impacts on exporting and importing companies.

이와 함께 글로벌 무역 환경 역시 경기 회복에 따른 교역 확대보다는 구조 재편과 선택적 성장이 중심이 되는 흐름으로 전환되고 있습니다. 주요국의 성장 둔화와 통상정책 불확실성이 지속되면서, 세계 교역 증가율은 제한적인 수준에 머물 가능성이 큽니다. 이에 따라 무역은 과거와 같은 동반 확대보다는 산업·지역별로 차별화된 흐름을 보일 것으로 전망됩니다.
산업 측면에서는 반도체·IT·첨단 제조업을 중심으로 한 교역은 비교적 견조한 흐름을 이어갈 가능성이 있는 반면, 전통 제조업과 범용 소비재 교역은 수요 둔화와 가격 경쟁 심화의 영향을 받을 수 있습니다. 지역별로는 미국·중국 중심의 양자 구도에서 벗어나, EU·아세안·인도 등 제3시장의 중요성이 점진적으로 확대되는 흐름이 이어질 가능성이 큽니다. 이러한 환경은 2026년 무역 조건이 단순한 수요 회복보다 가격·환율·구조 변수에 더 민감하게 반응하는 단계로 접어들었음을 시사합니다.
At the same time, the global trade environment is also shifting away from expansion driven by economic recovery toward a pattern centered on structural reconfiguration and selective growth. As growth slows across major economies and uncertainty surrounding trade policy persists, global trade growth is likely to remain constrained. As a result, trade is expected to follow differentiated trajectories by industry and region, rather than the broad and synchronized expansion seen in earlier periods.
From an industry perspective, trade related to semiconductors, IT, and advanced manufacturing is likely to maintain relatively resilient momentum. In contrast, traditional manufacturing sectors and general consumer goods trade may come under pressure from weaker demand and intensified price competition. From a regional perspective, the global trade structure is expected to gradually move beyond a framework centered on the United States and China, with the importance of third markets such as the EU, ASEAN, and India continuing to increase. Taken together, these conditions suggest that trade dynamics in 2026 are entering a stage in which price, exchange rate, and structural factors play a more decisive role than a simple recovery in demand.
2026년을 대비한 기업 전략 포인트
Key Corporate Strategy Points for 2026
2026년을 앞둔 글로벌 경제 환경에서 기업 전략의 핵심은 성장 기대보다는 변동성 관리와 선택적 대응에 놓여 있습니다. 무역 환경이 구조적으로 재편되고 환율 변동성이 상수로 자리 잡는 가운데, 기업들은 과거처럼 수요 회복에만 의존하기보다 시장·환율·공급망을 동시에 고려한 전략적 접근이 요구되는 국면에 진입했습니다.
As companies prepare for 2026, the core of corporate strategy is shifting away from growth expectations toward volatility management and selective responses. With the trade environment undergoing structural reconfiguration and exchange rate volatility becoming a constant factor, firms are entering a phase in which strategic approaches must simultaneously account for markets, exchange rates, and supply chains, rather than relying solely on demand recovery as in the past.

첫째, 수출 시장 다변화 전략의 중요성이 더욱 커지고 있습니다. 특정 국가나 시장에 대한 의존도가 높을수록 통상 정책 변화와 환율 변동의 영향이 증폭될 수 있기 때문에, 제3시장 비중 확대와 거래 구조 분산이 리스크 관리 측면에서 중요한 과제가 됩니다.
둘째, 환율을 고려한 가격·계약 구조 재점검이 필요합니다. 환율 변동성이 확대되는 환경에서는 단기 환율 예측보다, 환율 변화에 대응할 수 있는 가격 조정 메커니즘과 계약 조건 설계가 기업 수익성에 더 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
셋째, 조달·공급망 전략과 환율 대응의 연계가 요구됩니다. 핵심 부품과 원자재의 해외 의존도가 높은 산업일수록, 환율 변동은 원가 구조에 직접적인 영향을 미칩니다. 이에 따라 구매 전략과 환율 리스크 관리를 분리하기보다, 하나의 전략 축으로 통합해 접근할 필요가 있습니다.
결국 2026년을 대비한 기업 전략은 단기적인 경기 판단보다, 무역 환경 변화와 환율 변동성을 전제로 한 구조적 대응 능력에 의해 성과가 좌우될 가능성이 큽니다.
First, the importance of export market diversification strategies is continuing to increase. The greater a company’s dependence on a specific country or market, the more amplified the impact of changes in trade policy and exchange rate fluctuations becomes. As a result, expanding exposure to third markets and diversifying transaction structures have emerged as critical tasks from a risk management perspective.
Second, there is a growing need to reassess pricing and contract structures with exchange rate considerations in mind. In an environment of heightened exchange rate volatility, corporate profitability is influenced less by short term exchange rate forecasts and more by the design of pricing adjustment mechanisms and contract terms that can effectively respond to currency movements.
Third, stronger integration between sourcing and supply chain strategies and exchange rate management is required. In industries with high dependence on overseas sourcing for key components and raw materials, exchange rate fluctuations have a direct impact on cost structures. Accordingly, procurement strategies and exchange rate risk management should be approached as a single, integrated strategic framework rather than managed separately.
Ultimately, corporate performance in 2026 is likely to be determined not by short term economic assessments, but by a company’s structural capacity to respond to changes in the trade environment and exchange rate volatility.
선택과 집중의 해
A Year of Selection and Focus
지난 편에서 2025년 한국 수출입 흐름을 점검한 데 이어, 이번 글에서는 이를 출발점으로 2026년 세계 경제 전망과 환율, 무역 환경의 변화를 살펴보았습니다. 무역과 환율은 제조업 경쟁력을 좌우하는 핵심 변수로 작용하는 만큼, 2026년은 단순한 성장 기대보다는 ‘성장 둔화 속 선택과 집중의 해’가 될 전망입니다. 다음 편 EP.3에서는「AI 반도체 수요 확산과 첨단산업 공급망 구조 변화」를 주제로, AI 반도체 산업을 통해 제조업의 본질적 경쟁력을 다시 바라보는 시각을 공유할 예정이니 계속해서 관심 있게 지켜봐 주시기 바랍니다.
Following the previous installment, which reviewed Korea’s export and import trends in 2025, this article took that analysis as a starting point to examine the 2026 global economic outlook, along with expected changes in the exchange rate and trade environment. As trade and exchange rates play a decisive role in shaping manufacturing competitiveness, 2026 is likely to be defined less by expectations of growth and more as a year of selection and focus amid slowing growth.
In the next installment, EP.3, we will explore “The Expansion of AI Semiconductor Demand and Structural Changes in Advanced Industry Supply Chains,” sharing perspectives on how the AI semiconductor industry offers a new lens through which to reassess the fundamental competitiveness of manufacturing. We invite you to continue following the series with interest.




