“현장에선, 실제로 뭐가 어떻게 달라졌는데요?”
이번 글에서는 세미나 현장에서 소개된 공작기계 기반 AI 적용 사례들을 중심으로, 기술이 어떻게 ‘작동’하고 있고, 그 과정에서 어떤 변화와 문제들이 나타나고 있는지 살펴보겠습니다.
In the previous article, we explored why the keyword "autonomous manufacturing" is gaining attention in the machining industry, and where the technology currently stands. However, the question that many of you are probably most curious about is this.
"On the shop floor, what has actually changed?"
In this article, we’ll focus on real-world AI application cases in the machining industry, as presented at the seminar, to examine how the technology is actually operating, and the changes and challenges that have emerged along the way.

AI를 도입하고 싶다는 이야기는 많아졌지만, 막상 실제로 시작해보려 하면 늘 마주치는 게 있습니다.
바로 데이터 문제입니다. 기계를 똑똑하게 만들기 위해선 무언가를 '배우게 할' 데이터가 필요한데, 우리 공장엔 정작 그런 데이터가 얼마나 있고, 또 쓸 수 있는 상태인지부터 헷갈리기 시작하죠.
이번 세미나에서도 공작기계 기반 설비에 AI를 적용하려는 기업들이 어떤 데이터 문제를 겪었고, 그걸 어떻게 해결했는지에 대한 구체적인 사례들이 공유됐습니다. 본격적인 AI 적용 이전에 어떤 준비가 필요한지, 그리고 그 과정에서 어떤 시행착오가 있었는지 이야기를 시작해보겠습니다.
There’s no shortage of talk about wanting to implement AI, but when it comes time to actually get started, there's always one common challenge: the data issue.
To make machines smarter, you need data that can teach the system. But in many cases, it becomes unclear just how much of that data is available in our factories, and whether it’s in a usable format.
At the seminar, we heard specific examples of the data challenges faced by companies trying to apply AI to machining equipment, and how they solved them. In this article, we’ll discuss the preparations needed before implementing AI, and explore the trial-and-error process companies went through along the way.
1. 공작기계에 AI를 도입하려는데, 데이터가 없다?
No Data for AI in Machining?
AI는 데이터를 먹고 자라는 기술입니다. 하지만 공작기계 산업에서 이 당연한 전제가 가장 먼저 무너졌습니다. 발표자들은 한 목소리로 말했습니다.
“생각보다, 우리는 데이터 준비가 하나도 안 되어 있었습니다.”
먼저, 공작기계의 구조와 연식, 제조사마다 달라지는 센서 부착 위치, 데이터 포맷, 인터페이스는 데이터 수집 자체를 어렵게 만들었습니다. 같은 공장 안에 있어도, 기계마다 데이터를 꺼내는 방법이 전부 달랐기 때문입니다. 게다가 어렵게 수집한 데이터조차 AI 학습에는 바로 쓸 수 없었습니다. 어떤 게 ‘정상’이고 ‘이상’인지 구분이 안 되고, 데이터가 비정기적으로 쌓이거나, 특정 공정만 편향되게 기록되어 있는 경우도 많았습니다.
결국 데이터가 부족한 게 아니라, AI가 활용할 수 있는 ‘구조화된 데이터’가 부족했던 겁니다. 여기서부터는 기술보다 ‘현장 이해’가 중요해졌습니다.
AI 도입을 시도한 한 프로젝트에서는 작업자와 함께 공구 마모, 진동 이상 등의 상태를 직접 정의하고, 수집된 데이터를 정제하고 라벨링하는 작업부터 먼저 시작했습니다. 이후 AI가 학습할 수 있도록 데이터를 시계열로 잘라내고, 정규화하며 모델에 맞는 형식으로 바꾸는 등, 기술보다는 ‘데이터를 다루는 방식’에 집중했다고 합니다.
공작기계 AI는 결국 ‘데이터 설계’의 문제였습니다.
기계마다, 공정마다 다른 현장 맥락을 이해하지 않고서는 제대로 된 AI 시스템을 만들 수 없다는 사실이 확인된 셈입니다.
AI is a technology that thrives on data. However, this basic assumption quickly fell apart in the machining industry. The presenters spoke unanimously:
“We were much less prepared with data than we expected.”
First off, the structure, age, and manufacturer of machining equipment, as well as the varying sensor placements, data formats, and interfaces, made data collection itself a challenge. Even within the same factory, the way data was retrieved from each machine was completely different. Moreover, the data that was collected could not be used directly for AI training. It was difficult to distinguish between ‘normal’ and ‘abnormal’ data, often due to irregular data collection or specific processes being disproportionately recorded.
The real issue wasn’t a lack of data, but a lack of structured data that AI could utilize. From here on, it wasn’t about technology, but about understanding the shop floor that became crucial.
In one project where AI was introduced, the team worked with operators to directly define states like tool wear or abnormal vibrations. The process started with cleaning and labeling the data. The focus shifted from technology to how the data was handled—cutting the data into time-series, normalizing it, and formatting it for AI learning.
In the end, AI in machining was a problem of ‘data design’.
Without understanding the unique context of each machine and process, creating a proper AI system was impossible.
2.실제 공작기계 현장에서 AI는 어떻게 쓰이고 있을까
How is AI Being Used in Actual Machining Environments?
세미나 현장에서는 실제 공작기계 기반 제조 기업들의 AI 도입 사례가 소개되었습니다. 이들은 단순한 자동화를 넘어서 데이터 기반 판단과 예측 제어, AI 중심 의사결정으로 변화를 만들어가고 있었으며, 공통적으로 공정 품질의 편차 감소, 생산성 향상, 숙련자의 감각 의존 최소화와 같은 목표를 추구하고 있었습니다.
At the seminar, several real-world examples of AI implementation in machining-based manufacturing companies were presented. These companies are going beyond simple automation to incorporate data-driven decision-making, predictive control, and AI-driven decision-making to drive change. Common goals include reducing process variation, improving productivity, and minimizing reliance on the intuition of skilled operators.
[자동차 부품사 A사] – 가공 중 이상 소음 감지와 품질 이슈 선제 대응
[Automotive Parts Manufacturer A] – Early Detection of Abnormal Noise and Quality Issues
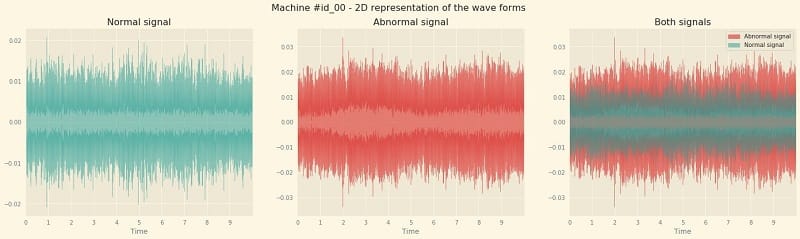
A사는 자동차용 기어 부품을 선삭하는 라인에 AI 기반의 이상 소음 감지 시스템을 도입했습니다. AI가 머신러닝 기반으로 가공 중 발생하는 소리 데이터를 실시간 분석하여, 비정상적 진동이나 소음이 감지되면 바로 알람을 발생시키는 구조입니다.
📌 도입 전: 불량 발생 후 검사로 확인 → 원인 추적 시점이 늦고 생산성 손실
📌 도입 후: 공정 중 실시간 감지 → 공정 중단 및 조치로 품질 손실 최소화
이 시스템은 오퍼레이터의 청각적 경험에 의존하던 방식에서 벗어나, 데이터 기반의 실시간 품질 모니터링 체계로 전환된 사례입니다.
Company A, a manufacturer of automotive gear parts, introduced an AI-based abnormal noise detection system on their turning line. The AI uses machine learning to analyze sound data generated during machining in real-time. If any abnormal vibrations or noises are detected, an alert is triggered immediately.
📌 Before implementation: Defects were identified only after inspection, causing delayed root cause analysis and productivity loss
📌 After implementation: Real-time detection during processing, allowing for immediate process stoppage and corrective actions, minimizing quality loss
This system shifted from relying on the operator's auditory experience to a data-driven real-time quality monitoring system.
[반도체 장비 부품사 B사] – AI가 추천하는 가공 조건
[Semiconductor Equipment Parts Manufacturer B] – AI-Recommended Machining Conditions

B사는 반도체 설비용 고정밀 부품을 다품종 소량으로 생산하는 공장으로, 제품별 조건 세팅 부담이 컸습니다. 이를 해결하기 위해 AI 기반 가공 조건 추천 시스템을 개발해 운영 중입니다.
작업자가 제품 도면 및 요구 조건을 입력하면, AI가 과거 유사 제품의 가공 이력과 품질 데이터를 분석해 초기 가공 조건(속도, 이송, 절입량 등)을 자동으로 제안하는 시스템 입니다. 이를 통해 초기 세팅 시간이 단축되었을 뿐 아니라, 첫 제품 가공부터 품질 안정도가 높아지는 효과를 얻었다고 말했습니다.
Company B manufactures high-precision parts for semiconductor equipment in small batches with various products. The challenge was managing the complexity of setting machining conditions for each product. To solve this, they developed and implemented an AI-based machining condition recommendation system.
When an operator inputs the product drawing and required specifications, the AI analyzes the machining history and quality data of similar products to automatically suggest initial machining conditions (such as speed, feed rate, and depth of cut). This not only shortened the initial setup time, but also improved the quality consistency from the first product produced.
[공작기계 부품사 C사] – 공구 마모 예측과 교체 타이밍 자동 판단
[Machining Parts Manufacturer C] – AI Predicts Tool Wear and Automatically Determines Replacement Timing

C사는 스핀들 부품을 가공하는 공장에서, 기존에는 경험 기반으로 공구 수명을 관리해왔습니다. 하지만 품질 편차와 불량 리스크가 문제였습니다. 이에 따라 AI가 실시간 가공 데이터를 분석해 공구의 마모 상태를 예측하고, 일정 임계치 도달 시 교체 타이밍을 자동으로 알리는 시스템을 도입했습니다.
📌 공구 과다 사용으로 인한 불량 감소
📌 불필요한 조기 교체 감소 → 공구 비용 최적화
이 시스템은 불량률을 10% 이상 줄였으며, 공정 안정성과 생산성 모두 개선되었다고 발표했습니다.
Company C, a manufacturer of spindle parts, previously managed tool life based on operator experience. However, this led to quality variation and defect risks. To address this, they introduced an AI system that analyzes real-time machining data to predict tool wear and automatically alerts when it’s time for tool replacement.
📌 Reduced defects caused by excessive tool usage
📌 Reduced unnecessary early replacements, optimizing tool costs
This system has helped reduce defect rates by over 10%, improving both process stability and productivity.
3.AI 도입의 현실: 겪어보니 보이는 과제들
The Reality of AI Adoption: The Challenges We Face
소개된 기업들은 모두 AI 도입을 통해 실질적인 개선 효과를 확인했지만, 동시에 공통적으로 다음과 같은 ‘현실적인 문제들’을 겪고 있다고 말했습니다.
The companies showcased at the seminar have all seen real improvements through AI adoption. However, they all shared some common challenges they faced in the process.
데이터는 많은데, 쓸 수가 없다?
Data: Plenty, but Not Usable
AI의 첫걸음은 ‘데이터’입니다. 하지만 현장에서는 의외로 이 데이터가 바로 쓸 수 있는 형태가 아닌 경우가 많습니다. 센서는 부착되어 있지만 이상값이 누락되거나, 각 공정에서 생성되는 데이터의 형식이 제각각이라 정합성이 떨어지고, 오랫동안 축적한 이력 데이터조차 라벨링이 되어있지 않아 학습에 사용할 수 없는 경우도 많습니다.
단순히 ‘데이터가 있다’는 것과 ‘AI가 학습 가능한 데이터가 있다’는 건 전혀 다르다는 점이 핵심 문제 중 하나입니다.
The first step in AI is data. However, surprisingly, in many cases, the data available on the shop floor is not in a usable form. While sensors are in place, there are often missing data points for abnormal values. Additionally, the data generated across different processes is in varied formats, leading to a lack of consistency. Even years of accumulated historical data may not be usable because it’s not labeled for learning purposes.
The key issue is that having data is very different from having AI-compatible data.
시스템 통합, 말처럼 쉽지 않다
System Integration: It’s Harder Than It Sounds
AI는 단독으로 동작하지 않습니다. 센서, 가공기, PLC, MES 등 다양한 장비와 시스템이 유기적으로 연결되어야 효과를 발휘할 수 있습니다. 하지만 실제 공장은 공정별로 사용 중인 장비 브랜드가 달라, 프로토콜이나 인터페이스가 상이하거나, 노후 장비는 데이터 출력 기능 자체가 없거나, 시스템 간 연동을 위한 엔지니어링 리소스 부족한 등 여러 문제가 산재해 있습니다.
따라서 AI 기술보다도, 이를 받아줄 인프라와 설비 통합의 어려움이 AI 도입을 가로막는 경우가 많습니다.
AI doesn't work in isolation. For AI to be effective, sensors, machining equipment, PLCs, MES, and other systems must be integrated and work together seamlessly. However, the reality of the factory floor is that different processes use different equipment brands, resulting in protocols or interfaces that don’t match. Older equipment may not even have data output capabilities, and there is often a lack of engineering resources to facilitate system integration.
Therefore, the real challenge isn’t the AI technology itself, but rather the infrastructure and equipment integration needed to support it.
AI를 어디에 어떻게 써야 하는지 막막하다
How and Where to Apply AI?
기술은 빠르게 진화하지만, 실제 현장에서 “우리 라인에 AI를 어떻게 적용하지?”라는 질문에 명확히 답할 수 있는 사람은 많지 않습니다. 이번 세미나 발표에서도 어떤 공정에 먼저 적용하는 게 좋은지, 어떤 데이터가 가장 먼저 정비되어야 하는지, 적용했을 때 얼마나 효과가 있을지 등 “초기에 AI의 방향 설정 자체가 어렵다”는 고민이 가장 많이 나왔습니다.
이는 단순 기술 도입이 아니라, 공정 구조와 목적에 맞는 AI 설계가 필요하다는 점을 강조하고 있습니다. 이런 현실적인 문제들 때문에, 기업들은 ‘기술 도입’보다도 “데이터를 어떻게 다루고, 어떤 역할을 맡길지를 먼저 정의해야 한다”는 교훈을 얻고 있었습니다.
Technology evolves rapidly, but when it comes to implementing AI, the question "where and how should we apply AI?" is not easily answered on the shop floor. One of the most common concerns shared during the seminar was how to set the direction for AI implementation—which process to apply it to first, which data should be prioritized for preparation, and how much of an impact it will have once implemented.
This highlights that AI adoption is not just about implementing technology, but about designing AI to fit the specific process structure and objectives.
Because of these challenges, companies are realizing that the first step isn’t just to adopt technology, but to define how to manage the data and assign roles before anything else.
4.혼자서는 어렵기에: 공공 지원과 협업의 필요성
It’s Hard to Do It Alone: The Need for Public Support and Collaboration

AI 기술이 빠르게 발전하고 있다는 건 모두가 알고 있습니다. 하지만 막상 우리 공정에 적용하려고 하면 이야기가 달라집니다. 설비마다 조건이 다르고, 필요한 데이터는 여기저기 흩어져 있으며, 내부에 AI 전문가도 부족한 것이 현실입니다.
이번 세미나에서는 “혼자 하기 어렵다”는 현장의 목소리에, 정부와 공공기관이 어떻게 응답하고 있는지를 확인할 수 있었습니다. 단순한 기술 설명을 넘어서, “어떻게 시작하고, 누구와 연결되어야 하는가”에 대한 구체적인 답이 나왔습니다.
AI technology is advancing rapidly, and that’s common knowledge. However, when it comes to actually applying it to our processes, the story changes. Equipment conditions vary, necessary data is scattered, and there’s often a lack of in-house AI expertise.
At the seminar, we got a clearer understanding of how the government and public institutions are responding to the "It's too difficult to do it alone" sentiment from the shop floor. The discussion went beyond simple technical explanations and provided specific answers to "Where to start and who to connect with."
정책의 방향은 ‘판단’의 자동화
The Policy Direction: Automating Decision-Making
정부의 자율제조 정책은 분명한 방향을 가지고 있습니다.
사람이 하던 판단을, AI가 하도록 바꾸는 것
이를 위해 산업용 로봇, 산업 AI, 산업용 소프트웨어 기술이 핵심 축으로 제시됩니다. AI가 단순 분석을 넘어, 실제 공정의 판단과 실행을 맡을 수 있도록 실증 중심의 프로젝트가 운영되고 있습니다.
The government’s approach to autonomous manufacturing is clear.
The goal is to have AI take over decision-making from humans.
To achieve this, three core technologies—industrial robots, industrial AI, and industrial software—have been identified. The government is running project-based initiatives to allow AI to take over the decision-making and execution in processes, rather than just performing analysis.
지원 방식도 다양하게
Diverse Support Methods
이번 발표에서 소개된 정부 지원은 두 가지 트랙으로 나뉩니다. 이 두 가지 모두 단독 기업 참여가 어려운 구조를 고려해 수요기업 + 공급기업 + 출연연 + 지자체가 함께 참여하는 협업 중심 모델로 설계되었습니다.
- 선도 프로젝트
- 약 80억 원 규모
- 앵커기업 중심의 대형 실증 과제 - 미니 프로젝트
- 약 3억 원 규모
- 공작기계 기반 AI 적용 사례 다수 포함
- 2024년부터 본격 운영
The government’s support, as introduced at the seminar, is divided into two main tracks. Both of these projects have been designed as collaborative models that involve not just individual companies, but also demand companies, supply companies, research institutes, and local governments.
- Lead Projects
- Approx. 8 billion KRW
- Large-scale implementation projects led by anchor companies - Mini Projects
- Approx. 300 million KRW
- Includes many AI application cases in machining
- Officially starting in 2024
기업에게 필요한 자세는?
What Does the Company Need to Do?
세미나에서 공유된 제언도 실질적이었습니다. 공급기업은 모델보다 실제 적용 경험을 강조해야하고, 수요기업은 왜 AI가 필요한지 기대효과를 명확히 해야하며, 컨소시엄 구성 시에는 전문기업을 포함해 지자체 연계 전략을 고려해야한다고 했습니다.
결국 핵심은 하나였습니다.
AI는 기술의 문제가 아니라, 연결의 문제다
혼자서는 어렵지만, 서로 연결된다면 현실화 가능성은 훨씬 높아집니다.
저희 오알에스코리아 역시, 이러한 구조 속에서 AI 기술을 실제 공작기계 기반 현장에 적용하기 위한 연구와 협업을 이어가고 있습니다. 단순한 기술 도입을 넘어, 현장에 스며드는 변화를 만들기 위해서입니다.
The suggestions shared at the seminar were very practical. Supply companies were advised to emphasize real-world application experience rather than just models. Demand companies were encouraged to clearly define why AI is necessary and the expected benefits. Additionally, when forming consortia, it’s important to include specialized companies and consider strategies for local government partnerships.
Ultimately, everything pointed to one key takeaway.
AI is not just a technological challenge; it’s a connection challenge.
It’s difficult to do it alone, but when we connect—the possibilities for turning these ideas into reality increase exponentially.
At ORSKOREA, we’re continuing our research and collaborations to help apply AI technology to machining industries. We aim to go beyond mere technology adoption, focusing on creating real change on the shop floor.
5.기술을 넘는 연결, 변화를 향한 작은 출발점
Beyond Technology, The First Step Towards Change

AI 기반 자율제조는 단순히 첨단 기술의 도입을 넘어, 산업 전체가 하나의 흐름으로 맞물려 가는 과정이었습니다. 한 기업의 기술만으로 해결할 수 없는 만큼, 공작기계 제조사, AI 전문 기업, 정책 기관이 함께 고민하고 연결되는 구조가 무엇보다 중요합니다.
저희 오알에스코리아도 그런 연결의 중심에서 현장의 실질적인 변화를 이끌 수 있는 기술 개발과 협업에 집중하고 있습니다. 기계가 ‘판단’하고, 공정이 ‘자율’적으로 움직이는 미래. 그 출발점은 결국, 지금 우리 공장에서 마주하고 있는 문제를 하나씩 정의하고 해결해 나가는 과정일 겁니다.
이번 글이 그 출발점을 고민하고 계신 분들께 하나의 현실적인 힌트이자, 다음 변화를 위한 실마리가 되었기를 바랍니다.
AI-driven autonomous manufacturing is not just about adopting cutting-edge technology; it’s a process of integrating the entire industry into a seamless flow. Since it cannot be solved by one company’s technology alone, the connection between machining manufacturers, AI specialists, and policy organizations is more important than ever.
At ORSKOREA, we are focusing on research and collaboration at the heart of this connection to drive real change on the shop floor. The future where machines make decisions and processes move autonomously begins with defining and solving the issues we face in our own factories one by one.
We hope this article serves as a practical clue for those contemplating that first step and as a starting point for the next phase of change.



